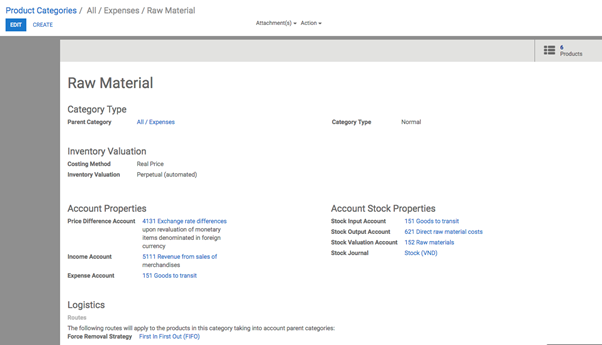
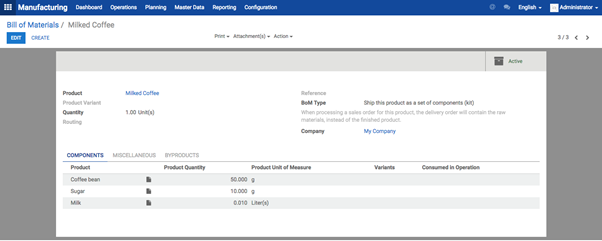
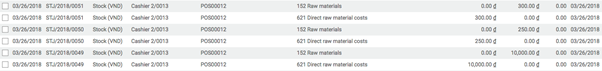
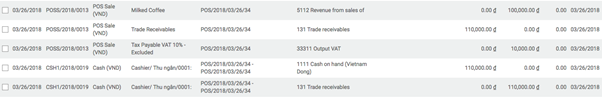
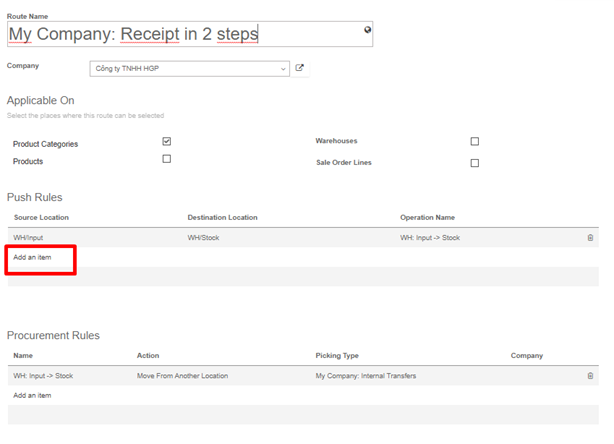
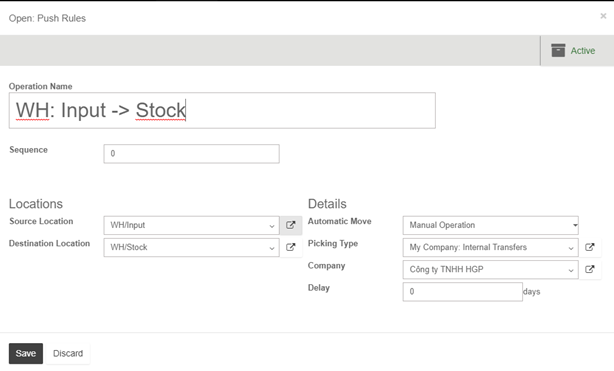
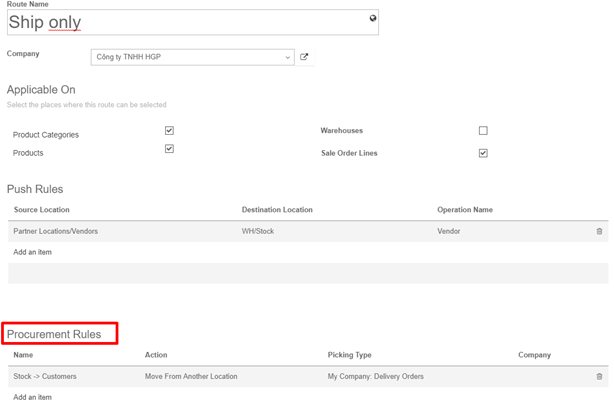
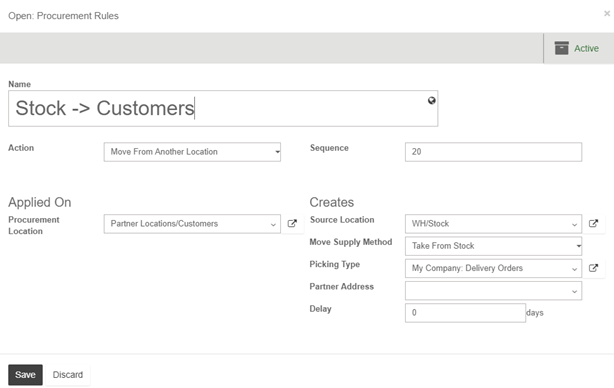
Removal strategies are usually in picking operations to select the best products in order to optimize the distance for the worker, for quality control purposes or due to reason of product expiration.
When a product movement needs to be done, the system will find available products that can be assigned to shipping. The way Kiu BMP assign these products depend on the removal strategy that is defined on the product category or on the location.
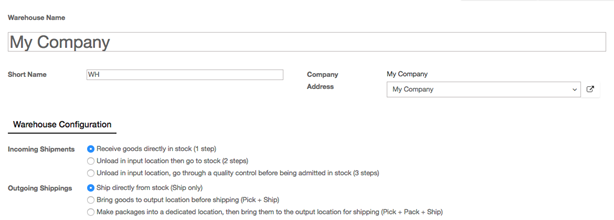
Go to Inventory -> Configuration -> Settings. Check Track lots or serial numbers, Manage several warehouses, each one composed by several by stock locations and Advanced routing of products using rules, then click on Apply.


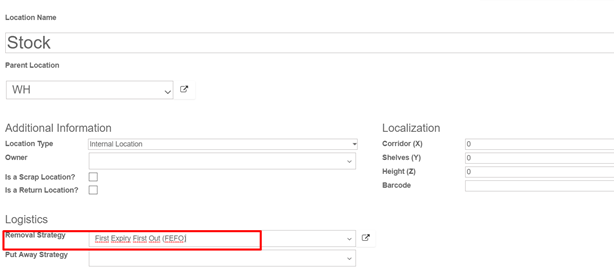
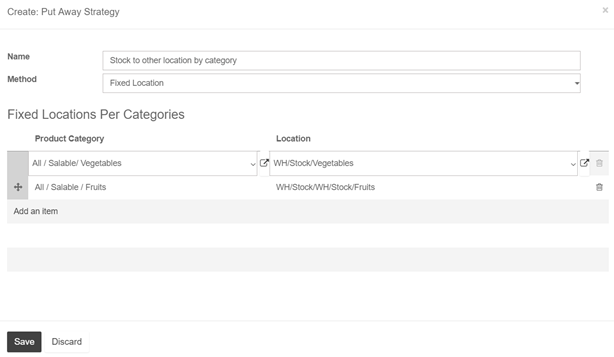
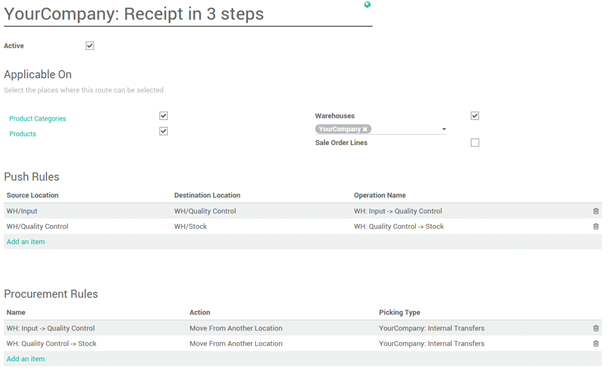
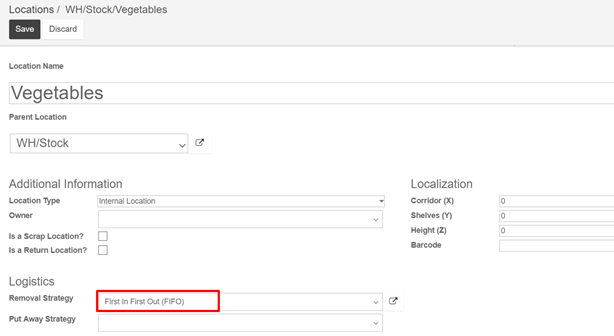
Then, open Configuration ‣ Locations and open the location on which you want to apply a removal strategy
-
Types of removal strategy
- First In First Out (FIFO)
A First In First Out strategy implies that the products that were stocked first will move out first. Companies should use FIFO method if they are selling perishable goods. Companies selling products with relatively short demand cycles, such as clothes, also may have to pick FIFO to ensure they are not stuck with outdated styles in inventory.
Go to Inventory ‣ Configuration ‣ Locations, open the stock location and set FIFO removal strategy.
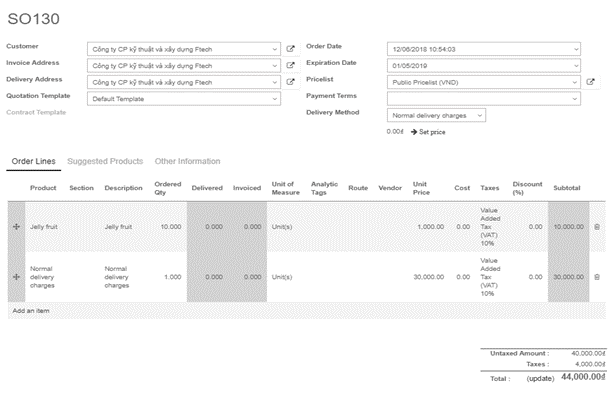
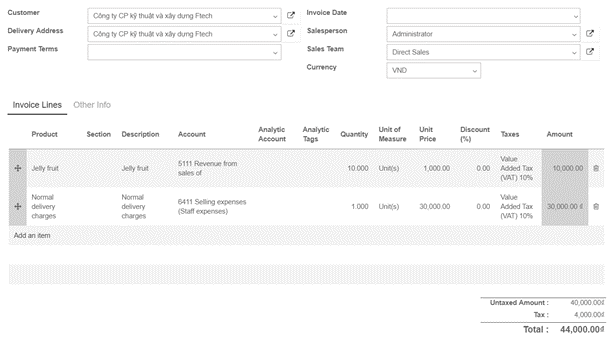
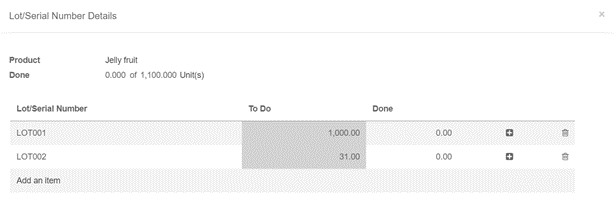
Let’s take one example of FIFO removal strategy.
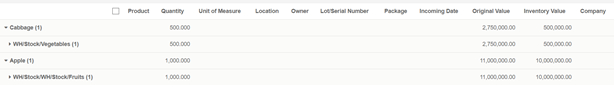
In your warehouse stock (WH/Stock) location, there are 2 lots of Jelly fruits available. You can find details of available inventory in inventory valuation report.

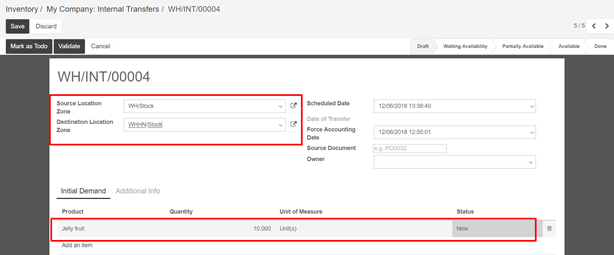
Create one sale order 1100 unit of Jelly fruit and confirm it. You can see in the outgoing shipment product that the Jelly fruit are assigned with the oldest lots, using the FIFO removal strategy.
- First Expiry First Out (FEFO)
In FEFO warehouse management, the products are dispatched from the warehouse according to their expiration date.
Go to Inventory ‣ Configuration ‣ Setting. Check the option Define Expiration date on serial numbers. Then click on Apply to save changes.

This will allow you to set four expiration fields for each lot or serial number: best before date, end of life date, alert date and removal date. These dates can be set from Inventory Control ‣ Lots/ Serial Numbers.
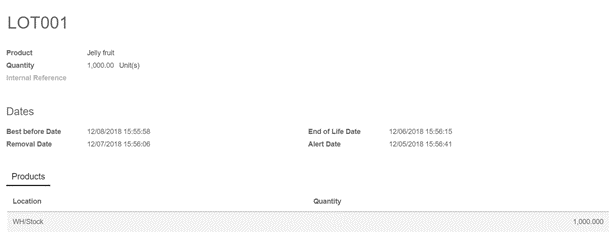
- Best Before Date: This is the date on which the goods with this serial/lot number start deteriorating, without being dangerous yet.
- End of Life Date: This is the date on which the goods with this serial/lot number may become dangerous and must not be consumed.
- Removal Date: This is the date on which the goods with this serial/lot number should be removed from the stock. Using the FEFO removal strategy, goods are picked for delivery orders using this date.
- Alert Date: This is the date on which an alert should be sent about the goods with this serial/lot number.
Lots will be picked based on their removal date, from earliest to latest. Lots without a removal date defined will be picked after lots with removal dates.
All dates except removal date are for informational and reporting purposes only. Lots that are past any or all of the above expiration dates may still be picked for delivery orders, and no alerts will be sent when lots pass their alert date.
Expiration dates on lots can also be set automatically when goods are received into stock. After enabling expiration dates on serial numbers, four new fields will become available in the inventory tab of the product form: product life time, product using time, product removal time, and product alert time. When an integer is entered into one of these fields, the expiration date of a lot/serial of the product in question will be set to the creation date of the lot/serial number plus the number of days entered in the time increment field. If the time increment field is set to zero, then the expiration date of a lot/serial must be defined manually after the lot has been created.
Each of these time increment fields is used to generate one of the lot expiration date fields as follows:
Product Use Time –> Best Before Date
Product Removal Time –> Removal Date
Product Life Time –> End of Life Date
Product Alert Time –> Alert Date
To set the removal strategy on location, go to Configuration ‣ Locations and choose FEFO