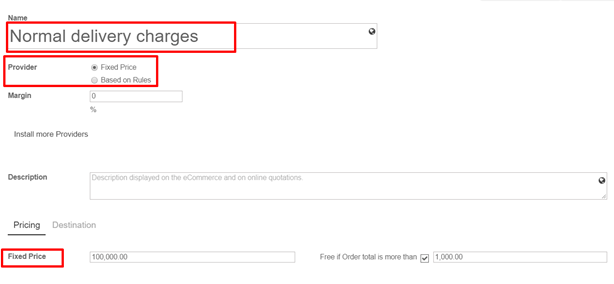
From Vendor Bill to Payment
Once vendor bills are registered in KIU BMP, you can easily pay vendors for the correct amount and at the right time (not too late, not too early; depending on your vendor policy). KIU BMP also offers reports to track your aged payable balances.
If you want to control vendor bills received from your vendors, you can use the KIU BMP Purchase application that allows you to control and pre-complete them automatically based on past purchase orders.
From Vendor Bill to Payment
Record a new vendor bill
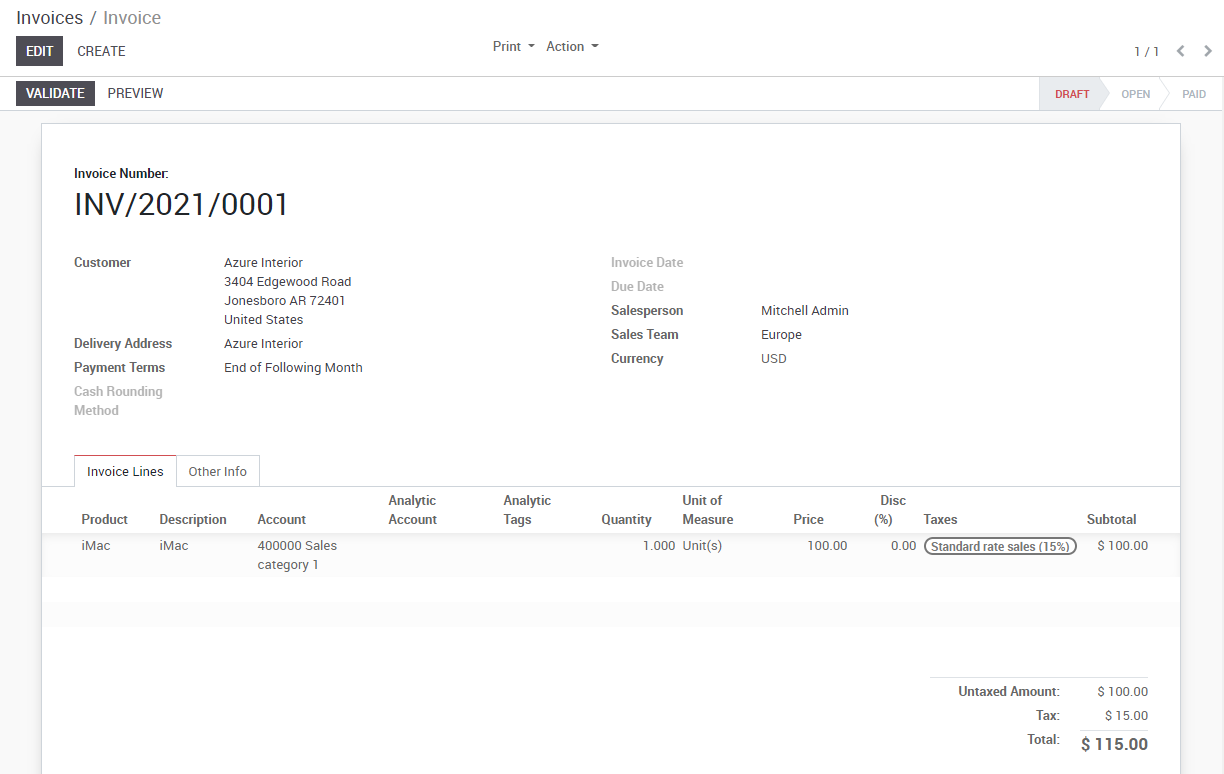
When a vendor bill is received, you can record it from Purchases ‣ Vendor Bills in the Accounting application. Some more in depth criteria book of ra online from intriquing,notable and useful information. As a shortcut, you can also use the New Bill feature on the accounting dashboard.
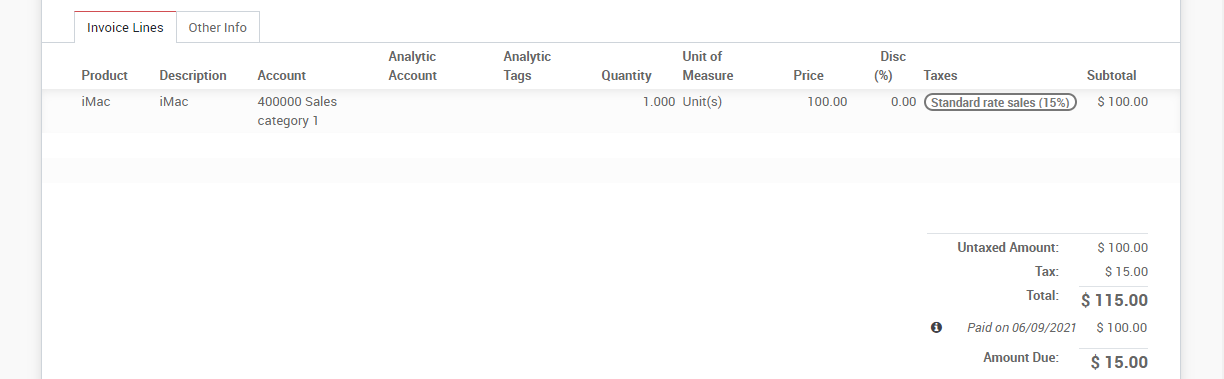
To register a new vendor bill, start by selecting a vendor and inputting their invoice as the Vendor Reference, then add and confirm the product lines, making sure to have the right product quantities, taxes and prices.
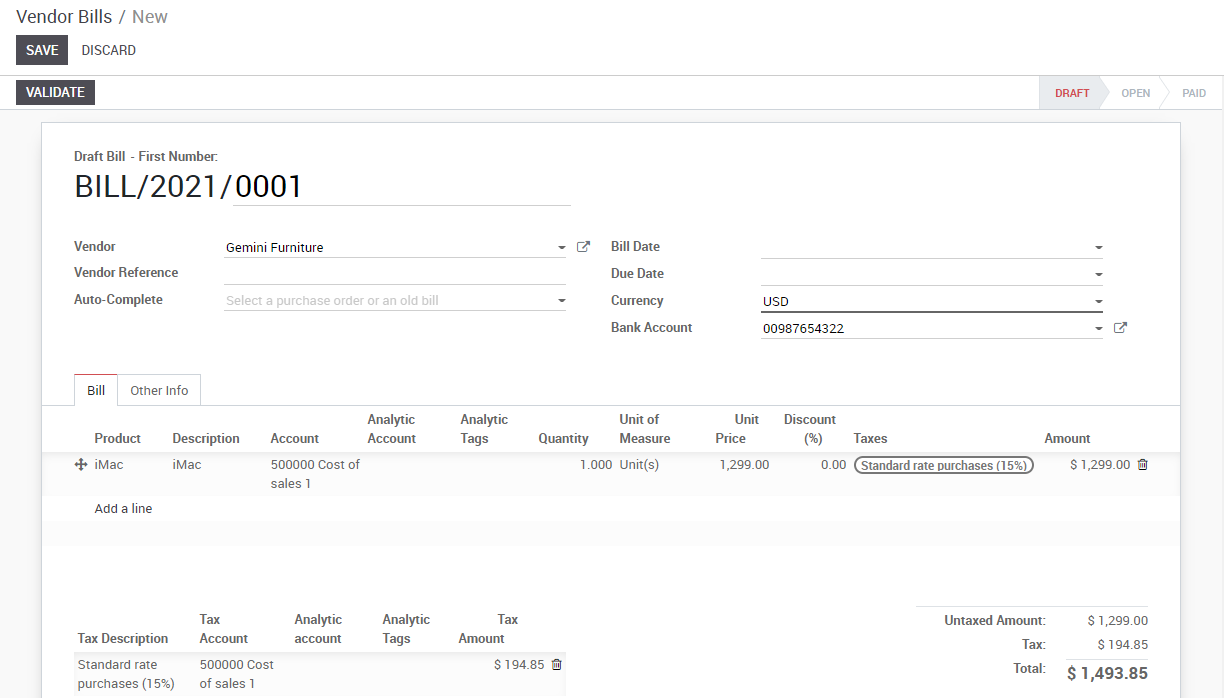
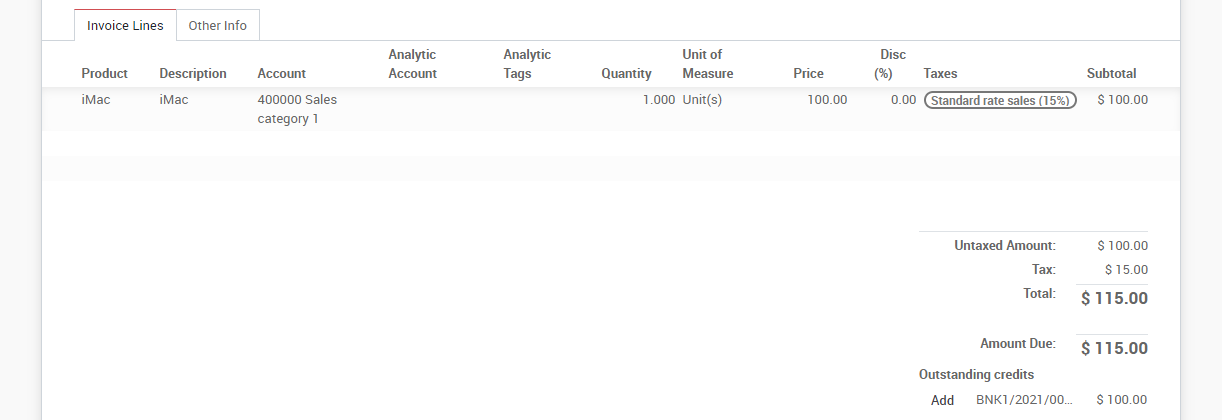
Save the invoice to update the pre tax and tax amounts at the bottom of the screen. You will most likely need to configure the prices of your products without taxes as KIU BMP will compute the tax for you.
Validate The Vendor Bill
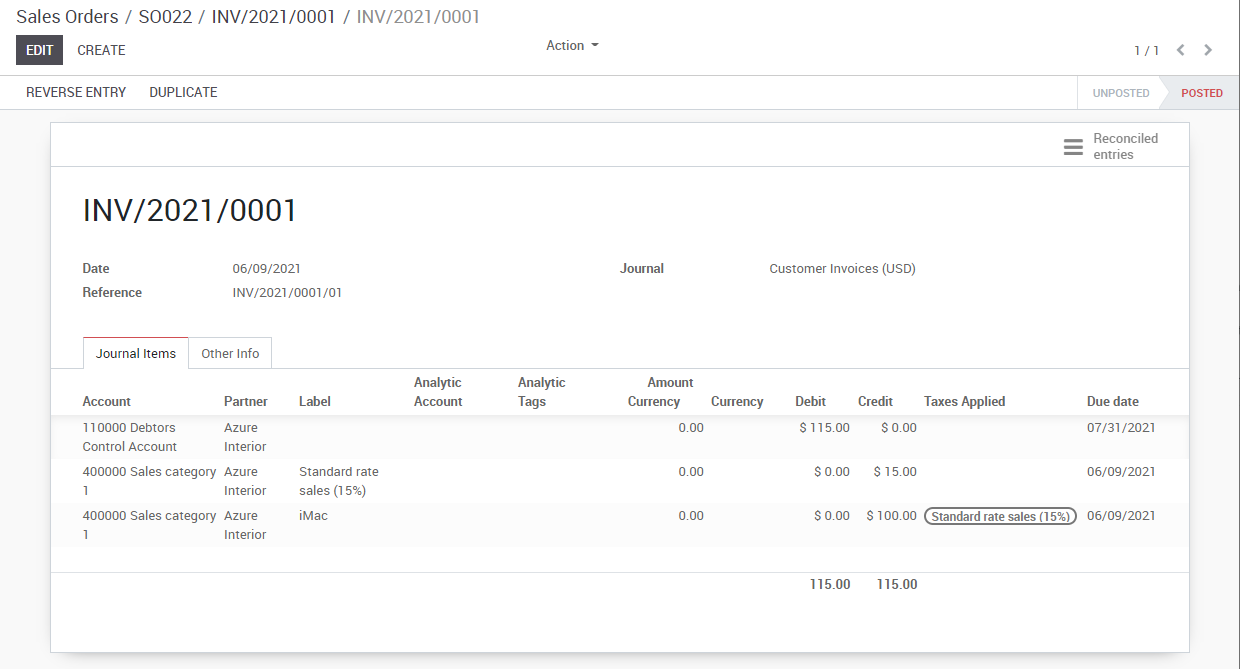
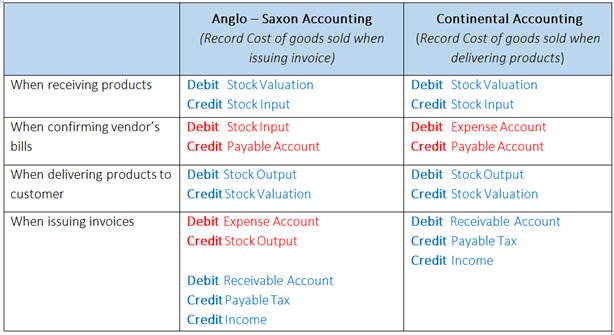
Once the vendor bill is validated, a journal entry will be generated based on the configuration on the invoice. This journal entry may differ depending on the the accounting package you choose to use.
For most European countries, the journal entry will use the following accounts:
- Accounts Payable: defined on the vendor form
- Taxes: defined on the products and per line
- Expenses: defined on the line item product used
For Anglo-Saxon (US) accounting, the journal entry will use the following accounts:
- Accounts Payable: defined on the vendor form
- Taxes: defined on the products and per line
- Goods Received: defined on the product form
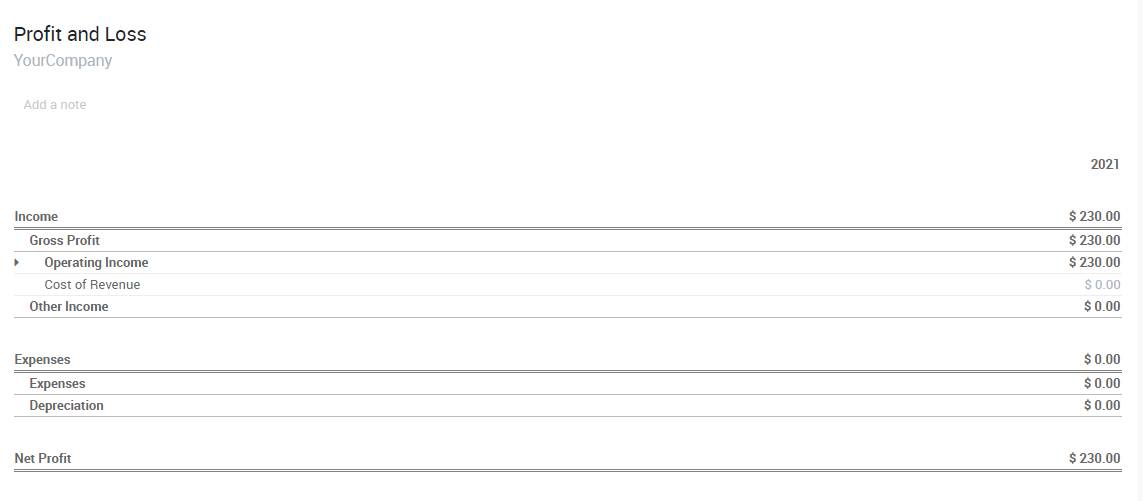
You can check your Profit & Loss or the Balance Sheet reports after having validated a couple of vendor bills to see the impact on your general ledger.
Pay a bill
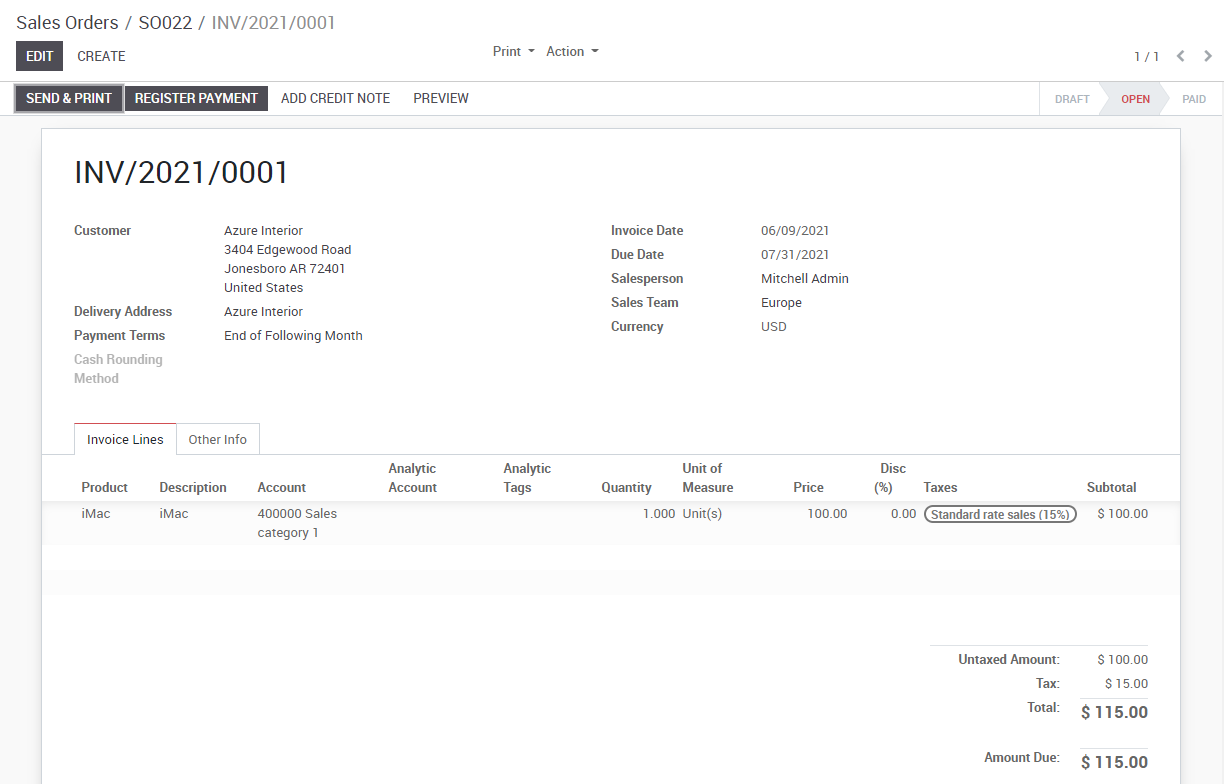
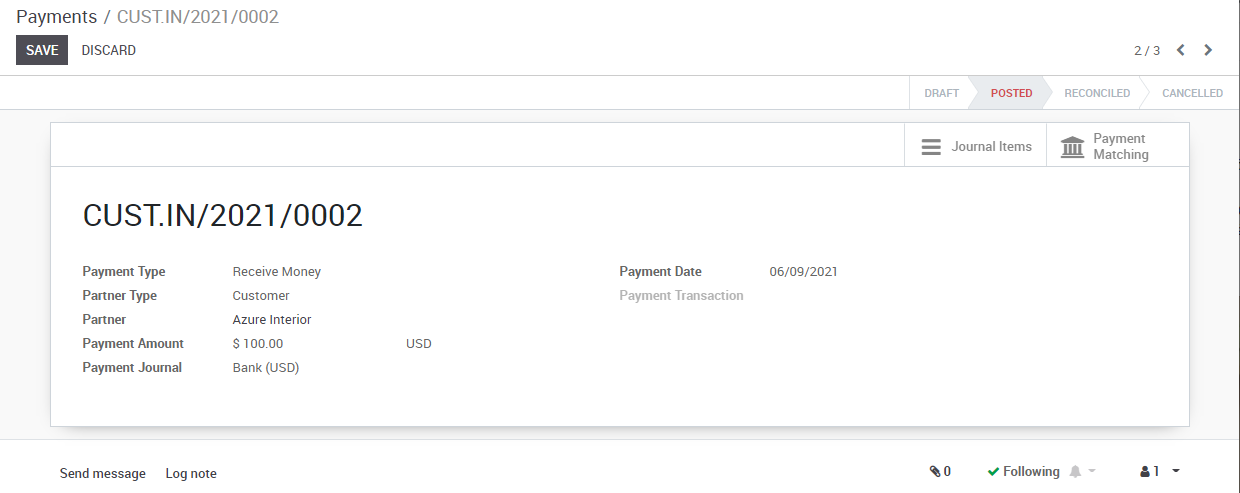
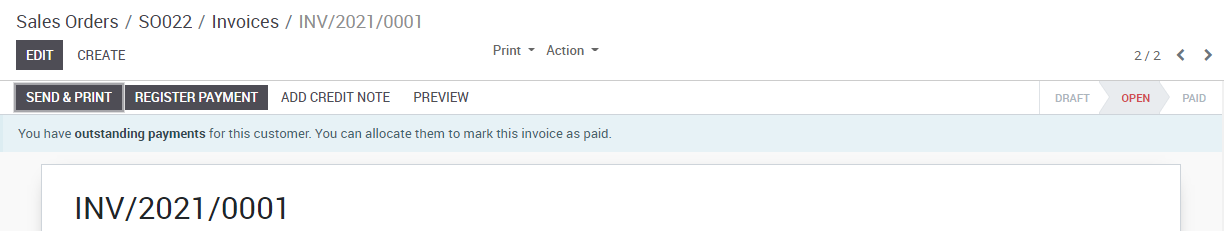
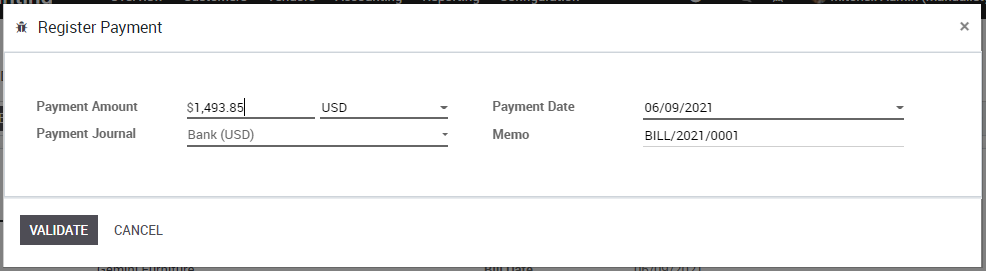
To create a payment for an open vendor bill directly, you can click on Register a Payment at the top of the form.
From there, you select the payment method (i.e. Checking account, credit card, check, etc…) and the amount you wish to pay. By default, KIU BMP will propose the entire remaining balance on the bill for payment. In the memo field, we recommend you set the vendor invoice number as a reference (KIU BMP will auto fill this field from the from the vendor bill if set it correctly).
Note
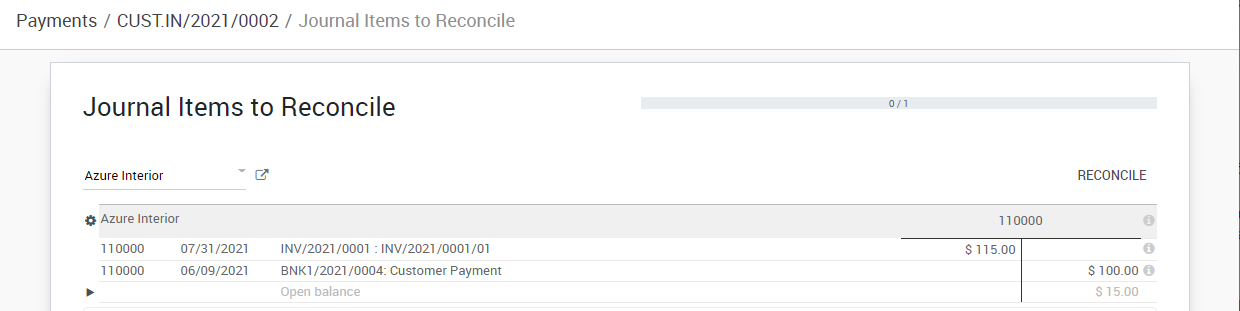
You can also register a payment to a vendor directly without applying it to a vendor bill. To do that, Purchases ‣ Payments. Then, from the vendor bill you will be able to reconcile this payment with directly.
Reporting
Aged payable balance
In order to get a list of open vendor bills and their related due dates, you can use the Aged Payable report, under the reporting menu, (in Reporting ‣ Business Statement ‣ Aged payable) to get a visual of all of your outstanding bills.
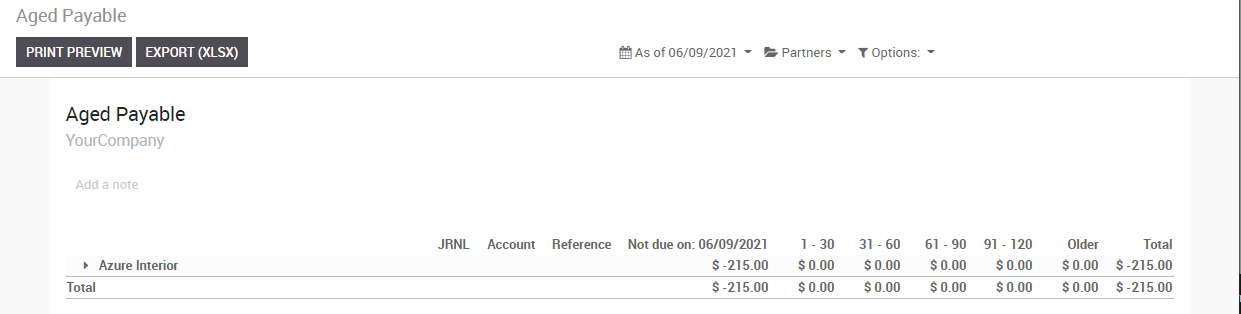
From here, you can click directly on a vendors name to open up the details of all outstanding bills and the amounts due, or you can annotate any line for managements information. At any point in time while you’re looking through the report, you can print directly to Excel or PDF and get exactly what you see on the screen.